Using Core Data to Save Data in an iOS App
This article describes the process of writing a to-do list application, and explains how to separate the data layer and the view layer in an iOS application, how to use Core Data to save data, and how to save the relationship between two data structures.
Prerequisites
Sample Code
Create an xcdatamodeld file
Create a new file of type "Data Model" in the Model folder.
Create Persistence.swift
Create a Persistence.swift file in the Data/Local folder, which defines the logic for accessing Core Data.
//
// Persistence.swift
// demo5-todo-list
//
// Created by arno_solo on 3/20/25.
//
import CoreData
struct PersistenceController {
static let shared = PersistenceController(dbName: "demo5_todo_list", appGroupsId: nil)
static let preview: PersistenceController = {
let result = PersistenceController(dbName: "demo5_todo_list", appGroupsId: nil, inMemory: true)
return result
}()
let container: NSPersistentContainer
init(dbName: String, appGroupsId: String? = nil, inMemory: Bool = false) {
container = NSPersistentContainer(name: dbName)
if let appGroupsId,
let appGroupsURL = FileManager.default.containerURL(forSecurityApplicationGroupIdentifier: appGroupsId) {
// Specify the URL for the persistent store
let storeURL = appGroupsURL.appendingPathComponent("\(dbName).sqlite")
// Set up the persistent store with the shared URL
container.persistentStoreDescriptions = [NSPersistentStoreDescription(url: storeURL)]
}
if inMemory {
container.persistentStoreDescriptions.first!.url = URL(fileURLWithPath: "/dev/null")
}
container.loadPersistentStores(completionHandler: { (storeDescription, error) in
if let error = error as NSError? {
print(error.localizedDescription)
}
})
container.viewContext.automaticallyMergesChangesFromParent = true
}
}Define Data Types
Define TodoModel in the Model folder, and then define a corresponding TodoEntity in the xcdatamodeld file.
import Foundation
struct TodoModel {
let todoId: String
let createdAt: Date
let updatedAt: Date
let title: String
let completedAt: Date?
let tags: [TagModel]
let location: LocationModel?
}Define DAO
Define a TodoDAO responsible for persisting TodoModel.
import CoreData
class TodoDAO {
enum CustomError: Error, LocalizedError {
case notFound
}
static let shared = TodoDAO(container: PersistenceController.shared.container)
private let container: NSPersistentContainer
init(container: NSPersistentContainer) {
self.container = container
}
func createOne(todo: TodoModel) async throws {
try await container.performBackgroundTask { ctx in
let entity = Self.findEntity(todoId: todo.todoId, ctx: ctx) ?? TodoEntity(context: ctx)
Self.modifyEntity(entity: entity, todo: todo)
try ctx.save()
}
}
func updateOne(todo: TodoModel) async throws {
try await container.performBackgroundTask { ctx in
guard let entity = Self.findEntity(todoId: todo.todoId, ctx: ctx) else {
throw CustomError.notFound
}
Self.modifyEntity(entity: entity, todo: todo)
entity.removeFromTags(entity.tags ?? [])
for tag in todo.tags {
if let tagEntity = TagDAO.findEntity(tagId: tag.tagId, ctx: ctx) {
entity.addToTags(tagEntity)
}
}
if let id = todo.location?.id {
entity.location = LocationDAO.findEntity(id: id, ctx: ctx)
} else {
entity.location = nil
}
try ctx.save()
}
}
func deleteOne(todoId: String) async throws {
return try await container.performBackgroundTask { ctx in
guard let entity = Self.findEntity(todoId: todoId, ctx: ctx) else {
throw CustomError.notFound
}
ctx.delete(entity)
try ctx.save()
}
}
func findOne(todoId: String) async -> TodoModel? {
return await container.performBackgroundTask { ctx in
guard let entity = Self.findEntity(todoId: todoId, ctx: ctx) else { return nil }
return Self.entityToModel(entity: entity, ctx: ctx)
}
}
// page: Start from 0
func findMany(searchInput: String?, tagId: String?, page: Int?, pageSize: Int?) async throws -> [TodoModel] {
let req = TodoEntity.fetchRequest()
// Search
var predicates: [NSPredicate] = []
if let searchInput, !searchInput.isEmpty {
// c: Case insensitive
// d: Diacritic insensitive
let predicate = NSPredicate(format: "title CONTAINS[cd] %@", searchInput)
predicates.append(predicate)
}
if let tagId {
let predicate = NSPredicate(format: "ANY tags.tagId == %@", tagId)
predicates.append(predicate)
}
// Pagination
if let page, let pageSize {
req.fetchLimit = pageSize
req.fetchOffset = page * pageSize
}
// Sort
req.sortDescriptors = [NSSortDescriptor(key: "updatedAt", ascending: false)]
return try await container.performBackgroundTask { ctx in
let entities = try ctx.fetch(req)
return entities.compactMap { Self.entityToModel(entity: $0, ctx: ctx) }
}
}
static func findEntity(todoId: String, ctx: NSManagedObjectContext) -> TodoEntity? {
do {
let req = TodoEntity.fetchRequest()
req.predicate = NSPredicate(format: "todoId = %@", todoId)
let entities = try ctx.fetch(req)
return entities.isEmpty ? nil : entities[0]
} catch {
print(error.localizedDescription)
return nil
}
}
static func modifyEntity(entity: TodoEntity, todo: TodoModel) {
entity.todoId = todo.todoId
entity.createdAt = todo.createdAt
entity.updatedAt = todo.updatedAt
entity.title = todo.title
entity.completedAt = todo.completedAt
}
static func entityToModel(entity: TodoEntity, ctx: NSManagedObjectContext) -> TodoModel? {
guard let todoId = entity.todoId,
let createdAt = entity.createdAt,
let updatedAt = entity.updatedAt,
let title = entity.title
else { return nil }
let tagEntities = entity.tags?.allObjects as? [TagEntity]
let tags: [TagModel] = (tagEntities ?? []).compactMap { entity in
TagDAO.entityToModel(entity: entity, ctx: ctx)
}
var location: LocationModel? = nil
if let locationEntity = entity.location {
location = LocationDAO.entityToModel(entity: locationEntity, ctx: ctx)
}
return TodoModel(
todoId: todoId,
createdAt: createdAt,
updatedAt: updatedAt,
title: title,
completedAt: entity.completedAt,
tags: tags,
location: location
)
}
}Relationships
Modify the .xcdatamodeld file
Many-to-many
- In the TodoEntity > Relationships interface, add a
tagsfield, and selectTagEntityas the Destination. Open the right sidebar > Relationship, and selectTo Manyas the Type. - In the TagEntity > Relationships interface, add a
todosfield, and selectTodoEntityas the Destination. Open the right sidebar > Relationship, and selectTo Manyas the Type. - Select TagEntity > Relationships > Inverse as
todos.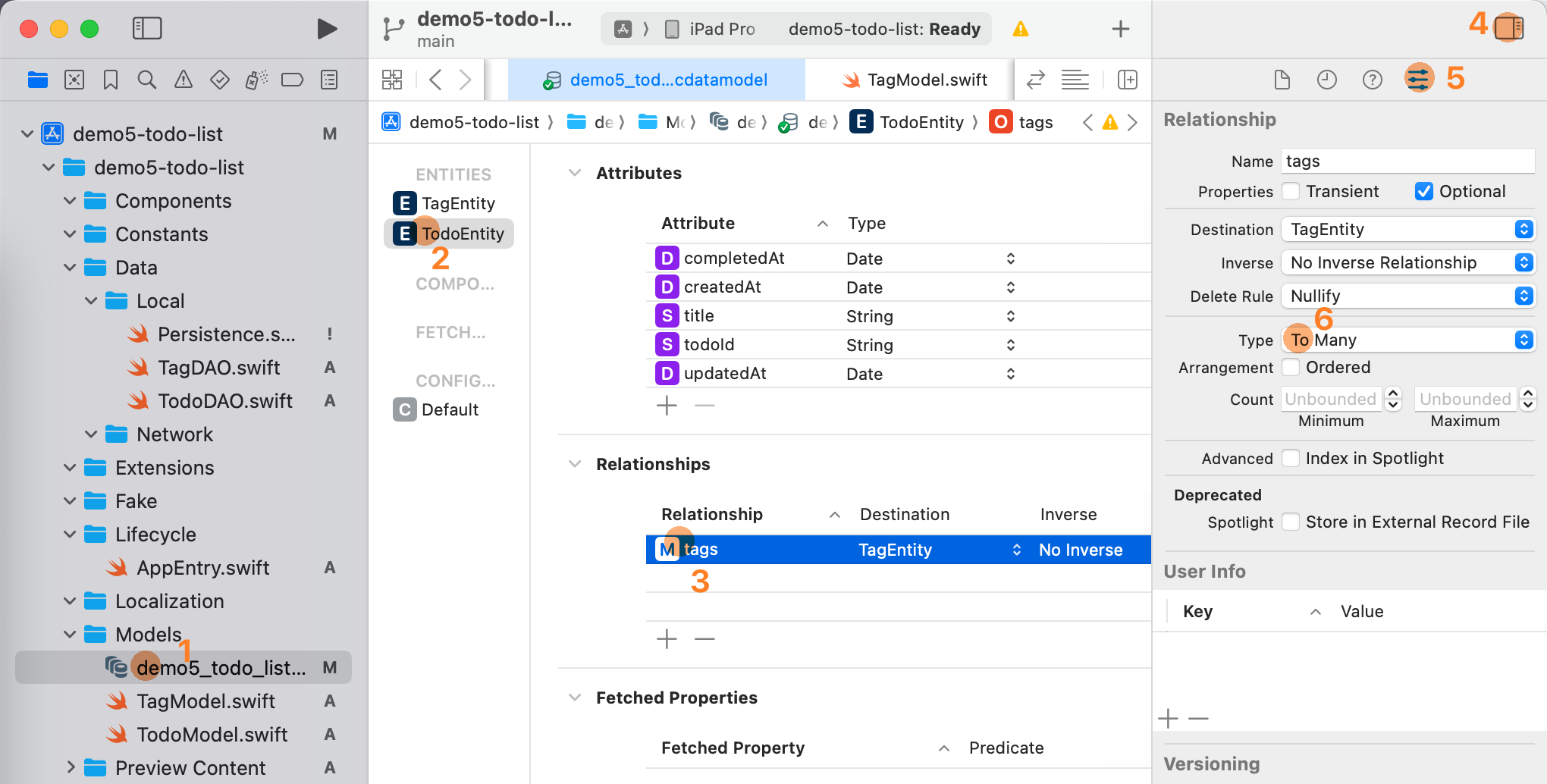
One-to-many
- In the TodoEntity > Relationships interface, add a
locationfield, and selectLocationEntityas the Destination. - In the LocationEntity > Relationships interface, add a
todosfield, and selectTodoEntityas the Destination. Open the right sidebar > Relationship, and selectTo Manyas the Type.
Writing
// Models/TodoModel.swift
class TodoDAO {
func updateOne(todo: TodoModel) async throws {
try await container.performBackgroundTask { ctx in
guard let entity = Self.findEntity(todoId: todo.todoId, ctx: ctx) else {
throw CustomError.notFound
}
Self.modifyEntity(entity: entity, todo: todo)
// Many-to-many
entity.removeFromTags(entity.tags ?? [])
for tag in todo.tags {
if let tagEntity = TagDAO.findEntity(tagId: tag.tagId, ctx: ctx) {
entity.addToTags(tagEntity)
}
}
// One-to-many
if let id = todo.location?.id {
entity.location = LocationDAO.findEntity(id: id, ctx: ctx)
} else {
entity.location = nil
}
try ctx.save()
}
}
}Reading
// Models/TodoModel.swift
class TodoDAO {
static func entityToModel(entity: TodoEntity, ctx: NSManagedObjectContext) -> TodoModel? {
guard let todoId = entity.todoId,
let createdAt = entity.createdAt,
let updatedAt = entity.updatedAt,
let title = entity.title
else { return nil }
let tagEntities = entity.tags?.allObjects as? [TagEntity]
let tags: [TagModel] = (tagEntities ?? []).compactMap { entity in
TagDAO.entityToModel(entity: entity, ctx: ctx)
}
var location: LocationModel? = nil
if let locationEntity = entity.location {
location = LocationDAO.entityToModel(entity: locationEntity, ctx: ctx)
}
return TodoModel(
todoId: todoId,
createdAt: createdAt,
updatedAt: updatedAt,
title: title,
completedAt: entity.completedAt,
tags: tags,
location: location
)
}
}Separating the Data Layer and the View Layer
My personal preference is:
- Define a
DAO(Data access object) for each data type. TheDAOis responsible for reading and writing to the local sqlite database. - Define a
Servicefor each backend service. TheServiceis responsible for communicating with the remote database. - Define a
Repositoryfor each data type. TheRepositoryis responsible for coordinating whether data is obtained from the local database or the remote database. - In the view, try to read and write data by calling the
Repositoryinstead of theDAOorService.
Here is an example of a file structure:
Data/
Local/
TodoDAO.swift
TagDAO.swift
Network/
FirestoreService.swift
TodoRepository.swift
TagRepository.swiftThe following is the code for TodoRepository. Currently, it only has code for reading and writing to the local database. If there is server request code in the future, it can also be written in this class.
import Foundation
class TodoRepository {
static let shared = TodoRepository(
todoDAO: TodoDAO.shared,
tagDAO: TagDAO.shared
)
private var todoDAO: TodoDAO
private var tagDAO: TagDAO
init(todoDAO: TodoDAO, tagDAO: TagDAO) {
self.todoDAO = todoDAO
self.tagDAO = tagDAO
}
func createTodo(todo: TodoModel) async throws {
try await todoDAO.createOne(todo: todo)
try await todoDAO.updateOne(todo: todo)
}
func updateTodo(todo: TodoModel) async throws {
try await todoDAO.updateOne(todo: todo)
}
func deleteTodo(todo: TodoModel) async throws {
try await todoDAO.deleteOne(todoId: todo.todoId)
}
func findTodos(searchText: String?, tagId: String?, page: Int?, pageSize: Int?) async throws -> [TodoModel] {
return try await todoDAO.findMany(searchInput: searchText, tagId: tagId, page: page, pageSize: pageSize)
}
}References